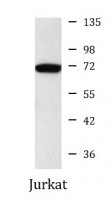
ARG55913
anti-Lamin B2 antibody
anti-Lamin B2 antibody for Immunoprecipitation,Western blot and Human,Mouse
Overview
| Product Description | Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes Lamin B2 |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu, Ms |
| Tested Application | IP, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Target Name | Lamin B2 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant Human Lamin B2 protein. |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | Lamin-B2; LMN2; LAMB2 |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Buffer | PBS (pH 7.4), 0.03% Proclin-300 and 50% Glycerol |
| Preservative | 0.03% Proclin-300 |
| Stabilizer | 50% Glycerol |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | LMNB2 |
| Gene Full Name | lamin B2 |
| Background | This gene encodes a B type nuclear lamin. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins located next to the inner nuclear membrane. The lamin family of proteins make up the matrix and are highly conserved in evolution. During mitosis, the lamina matrix is reversibly disassembled as the lamin proteins are phosphorylated. Lamin proteins are thought to be involved in nuclear stability, chromatin structure and gene expression. Vertebrate lamins consist of two types, A and B. Mutations in this gene are associated with acquired partial lipodystrophy. [provided by RefSeq, May 2012] |
| Function | Lamins are components of the nuclear lamina, a fibrous layer on the nucleoplasmic side of the inner nuclear membrane, which is thought to provide a framework for the nuclear envelope and may also interact with chromatin. [UniProt] |
| Cellular Localization | Nucleus inner membrane; Lipid-anchor; Nucleoplasmic side. |
| Calculated MW | 70 kDa |
| PTM | B-type lamins undergo a series of modifications, such as farnesylation and phosphorylation. Increased phosphorylation of the lamins occurs before envelope disintegration and probably plays a role in regulating lamin associations. |
Images (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In