ARG42294
anti-NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 antibody [7.1] (PE)
anti-NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 antibody [7.1] (PE) for Flow cytometry and Human
Overview
| Product Description | PE-conjugated Mouse Monoclonal antibody [7.1] recognizes NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Tested Application | FACS |
| Specificity | The mouse monoclonal antibody 7.1 recognizes an extracellular epitope of NG2, the melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 of Mw approximately 220-300 kDa. |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | 7.1 |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Target Name | NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Human bone marrow stromal cells infected with SV-40. |
| Conjugation | PE |
| Alternate Names | HMW-MAA; MCSPG; Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan NG2; MCSP; Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4; MSK16; NG2; Melanoma chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan; MEL-CSPG; Melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Purified |
| Buffer | PBS and 15 mM Sodium azide. |
| Preservative | 15 mM Sodium azide |
| Storage Instruction | Aliquot and store in the dark at 2-8°C. Keep protected from prolonged exposure to light. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links |
Swiss-port # Q6UVK1 Human Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | CSPG4 |
| Gene Full Name | chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 |
| Background | A human melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan plays a role in stabilizing cell-substratum interactions during early events of melanoma cell spreading on endothelial basement membranes. CSPG4 represents an integral membrane chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan expressed by human malignant melanoma cells. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Function | Proteoglycan playing a role in cell proliferation and migration which stimulates endothelial cells motility during microvascular morphogenesis. May also inhibit neurite outgrowth and growth cone collapse during axon regeneration. Cell surface receptor for collagen alpha 2(VI) which may confer cells ability to migrate on that substrate. Binds through its extracellular N-terminus growth factors, extracellular matrix proteases modulating their activity. May regulate MPP16-dependent degradation and invasion of type I collagen participating in melanoma cells invasion properties. May modulate the plasminogen system by enhancing plasminogen activation and inhibiting angiostatin. Functions also as a signal transducing protein by binding through its cytoplasmic C-terminus scaffolding and signaling proteins. May promote retraction fiber formation and cell polarization through Rho GTPase activation. May stimulate alpha-4, beta-1 integrin-mediated adhesion and spreading by recruiting and activating a signaling cascade through CDC42, ACK1 and BCAR1. May activate FAK and ERK1/ERK2 signaling cascades. [UniProt] |
| Cellular Localization | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein; Extracellular side. Apical cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein; Extracellular side. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein; Extracellular side. Cell surface. Note=Localized at the apical plasma membrane it relocalizes to the lamellipodia of astrocytoma upon phosphorylation by PRKCA. Localizes to the retraction fibers. Localizes to the plasma membrane of oligodendrocytes. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 251 kDa |
| PTM | O-glycosylated; contains glycosaminoglycan chondroitin sulfate which are required for proper localization and function in stress fiber formation (By similarity). Involved in interaction with MMP16 and ITGA4. Phosphorylation by PRKCA regulates its subcellular location and function in cell motility. [UniProt] |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In
-
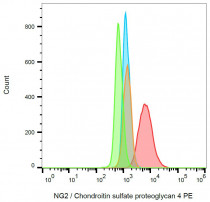
ARG42294 anti-NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 antibody [7.1] (PE) FACS image
Flow Cytometry: SK-MEL-30 cells stained with ARG42294 anti-NG2 / Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 antibody [7.1] (PE) (red; blank: orange). SP2 cells (negative sample) stained with the same antibody (blue; blank: green).