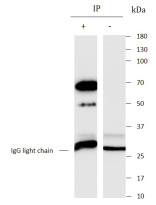
ARG44748
anti-Synaptotagmin antibody
anti-Synaptotagmin antibody for Immunoprecipitation,Western blot and Human,Rat
Overview
| Product Description | Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes Synaptotagmin |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu, Rat |
| Tested Application | IP, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Target Name | Synaptotagmin |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | P65; Synaptotagmin I; SytI; SVP65; SYT; p65; Synaptotagmin-1 |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Protein A purification |
| Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | SYT1 |
| Gene Full Name | synaptotagmin I |
| Background | The synaptotagmins are integral membrane proteins of synaptic vesicles thought to serve as Ca(2+) sensors in the process of vesicular trafficking and exocytosis. Calcium binding to synaptotagmin I participates in triggering neurotransmitter release at the synapse |
| Function | May have a regulatory role in the membrane interactions during trafficking of synaptic vesicles at the active zone of the synapse. It binds acidic phospholipids with a specificity that requires the presence of both an acidic head group and a diacyl backbone. A Ca(2+)-dependent interaction between synaptotagmin and putative receptors for activated protein kinase C has also been reported. It can bind to at least three additional proteins in a Ca(2+)-independent manner; these are neurexins, syntaxin and AP2. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 83 kDa |
| PTM | Proteolytically cleaved in the extracellular matrix by specific proteinases (possibly MMPs) in several cell lines and tumors. N- and O-glycosylated. O-glycosylation contains more-or-less-sulfated chondroitin sulfate glycans, whose number may affect the accessibility of specific proteinases to their cleavage site(s). It is uncertain if O-glycosylation occurs on Thr-637 or Thr-638. Phosphorylated; activation of PKC results in the dephosphorylation of Ser-706 (constitutive phosphorylation site), and the phosphorylation of Ser-672. |
Images (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In