ARG54069
anti-eEF2 antibody
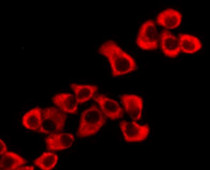
anti-eEF2 antibody for ICC/IF,Western blot and Human
Gene Regulation antibody
Overview
| Product Description | Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes EEF2 |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Tested Application | ICC/IF, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Target Name | eEF2 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant human eEF2 protein fragments expressed in E.coli. |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | EEF-2; EF2; EF-2; Elongation factor 2; SCA26 |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||||
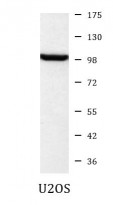
| Observed Size | 95 kDa |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity purified |
| Buffer | 0.1M Tris-Glycine (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 0.2% Sodium azide and 50% Glycerol |
| Preservative | 0.2% Sodium azide |
| Stabilizer | 50% Glycerol |
| Concentration | 0.4 mg/ml |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | EEF2 |
| Gene Full Name | eukaryotic translation elongation factor 2 |
| Background | Catalyzes the GTP-dependent ribosomal translocation step during translation elongation. During this step, the ribosome changes from the pre-translocational (PRE) to the post-translocational (POST) state as the newly formed A-site-bound peptidyl-tRNA and P-site-bound deacylated tRNA move to the P and E sites, respectively. Catalyzes the coordinated movement of the two tRNA molecules, the mRNA and conformational changes in the ribosome. |
| Function | Catalyzes the GTP-dependent ribosomal translocation step during translation elongation. During this step, the ribosome changes from the pre-translocational (PRE) to the post-translocational (POST) state as the newly formed A-site-bound peptidyl-tRNA and P-site-bound deacylated tRNA move to the P and E sites, respectively. Catalyzes the coordinated movement of the two tRNA molecules, the mRNA and conformational changes in the ribosome. [UniProt] |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm |
| Research Area | Gene Regulation antibody |
| Calculated MW | 95 kDa |
| PTM | Phosphorylation by EF-2 kinase completely inactivates EF-2; it requires prior phosphorylation by CDK2 at Ser-595 during mitotic prometaphase. Phosphorylation by CSK promotes SUMOylation, proteolytic cleavage, and nuclear translocation if the C-terminal fragment. Diphthamide is 2-[3-carboxyamido-3-(trimethyl-ammonio)propyl]histidine. Diphthamide can be ADP-ribosylated by diphtheria toxin and by Pseudomonas exotoxin A, thus arresting protein synthesis (By similarity). ISGylated. Proteolytically processed at two sites following phosphorylation by CSK. SUMOylated following phosphorylation by CSK, promotes proteolytic cleavage. |
Images (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In