ARG83004
arigoPLEX® Rat Inflammatory Cytokine Multiplex ELISA Kit (IL1 beta, IL6, IL10, TNF alpha)
arigoPLEX® Rat Inflammatory Cytokine Multiplex ELISA Kit (IL1 beta, IL6, IL10, TNF alpha) for ELISA and Rat
Component
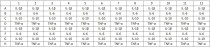
| Cat No | Component Name | Package | Temp |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARG83004-01 | Antibody Coated Microplate | 8 X 12 strips | 4°C |
| ARG83004-02 | Standards Mixture | 2 vials | 4°C |
| ARG83004-03 | 10X Antibody Conjugate Mixture | 1.2 ml | ≤ -20°C |
| ARG83004-04 | 40X HRP-Streptavidin Solution | 300 μl | 4°C |
| ARG83004-05 | Standard/Sample Diluent Buffer | 30 ml | 4°C |
| ARG83004-06 | Antibody Diluent Buffer | 35 ml | 4°C |
| ARG83004-07 | Serum Diluent Buffer | 10 ml | 4°C |
| ARG83004-08 | 20X Wash Buffer | 45 ml | 4°C |
| ARG83004-09 | TMB substrate | 12 ml | 4°C (protect from light) |
| ARG83004-10 | STOP solution | 12 ml | 4°C |
| ARG83004-11 | Plate sealer | 3 adhesive strips | Room temperature |
Overview
| Product Description | ARG83004 arigoPLEX® Rat Inflammatory Cytokine Multiplex ELISA Kit (IL1 beta, IL6, IL10, TNF alpha) is an Enzyme Immunoassay kit for the quantification of Rat Inflammatory Cytokine (IL1 beta, IL6, IL10, TNF alpha) in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. See all Multiplex ELISA kits |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Rat |
| Tested Application | ELISA |
| Target Name | Inflammatory Cytokine |
| Conjugation | HRP |
| Conjugation Note | Substrate: TMB and read at 450 nm. |
| Sensitivity | IL1 beta: 62.5 pg/ml IL6: 125 pg/ml IL10: 62.5 pg/ml TNF alpha: 62.5 pg/ml |
| Sample Type | Serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. |
| Standard Range | IL1 beta: 125 - 4000 pg/ml IL6: 250 - 8000 pg/ml IL10: 125 - 4000 pg/ml TNF alpha: 125 - 4000 pg/ml |
| Sample Volume | 25 µl |
Application Instructions
| Assay Time | 5 hours |
|---|
Properties
| Form | 96 well |
|---|---|
| Storage Instruction | Store components at 4°C or -20°C. Do not expose test reagents to heat, sun or strong light during storage and usage. Please refer to the product user manual for detail temperatures of the components. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Gene Symbol | Il1b; Il6; Il10; Tnf |
|---|---|
| Highlight | Related Product: IL1 beta antibodies; IL6 antibodies; IL10 antibodies; TNF alpha antibodies; Related news: Rat Inflammatory Cytokine Multiplex ELISA Kit for in vivo screening anti-inflammatory drugs; |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In
Specific References
| Title | Download Link |
|---|---|
| ARG83004 arigoPLEX® Rat Inflammatory Cytokine Multiplex ELISA Kit (IL1 beta, IL6, IL10, TNF alpha) User manual |
 Download Download
|