ARG66310
anti-ACMSD antibody
anti-ACMSD antibody for Western blot and Human
Overview
| Product Description | Rabbit Polyclonal antibody recognizes ACMSD |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Tested Application | WB |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Target Name | ACMSD |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of Human ACMSD. |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | EC 4.1.1.45; Picolinate carboxylase; 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate-6-semialdehyde decarboxylase |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||
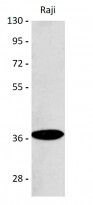
| Positive Control | WB: Raji cells. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity purification with immunogen. |
| Buffer | PBS (pH 7.4), 0.05% Sodium azide and 40% Glycerol. |
| Preservative | 0.05% Sodium azide |
| Stabilizer | 40% Glycerol |
| Concentration | 0.8 mg/ml |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links |
Swiss-port # Q8TDX5 Human 2-amino-3-carboxymuconate-6-semialdehyde decarboxylase |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | ACMSD |
| Gene Full Name | aminocarboxymuconate semialdehyde decarboxylase |
| Background | The neuronal excitotoxin quinolinate is an intermediate in the de novo synthesis pathway of NAD from tryptophan, and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several neurodegenerative disorders. Quinolinate is derived from alpha-amino-beta-carboxy-muconate-epsilon-semialdehyde (ACMS). ACMSD (ACMS decarboxylase; EC 4.1.1.45) can divert ACMS to a benign catabolite and thus prevent the accumulation of quinolinate from ACMS.[supplied by OMIM, Oct 2004] |
| Function | Converts alpha-amino-beta-carboxymuconate-epsilon-semialdehyde (ACMS) to alpha-aminomuconate semialdehyde (AMS). ACMS can be converted non-enzymatically to quinolate (QA), a key precursor of NAD, and a potent endogenous excitotoxin of neuronal cells which is implicated in the pathogenesis of various neurodegenerative disorders. In the presence of ACMSD, ACMS is converted to AMS, a benign catabolite. ACMSD ultimately controls the metabolic fate of tryptophan catabolism along the kynurenine pathway. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 38 kDa |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In