ARG58421
anti-CHRNA10 antibody
anti-CHRNA10 antibody for IHC-Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections,Western blot and Human
Overview
| Product Description | Rabbit Polyclonal antibody recognizes CHRNA10 |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Predict Reactivity | Rat |
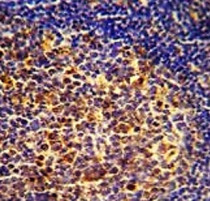
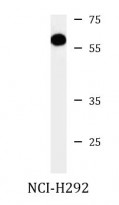
| Tested Application | IHC-P, WB |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Target Name | CHRNA10 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide corresponding to aa. 179-206 (Center) of Human CHRNA10. |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | NACHR alpha-10; Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-10; Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-10 |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||||
| Positive Control | NCI-H292 |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Purification with Protein A and immunogen peptide. |
| Buffer | PBS and 0.09% (W/V) Sodium azide. |
| Preservative | 0.09% (W/V) Sodium azide. |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links |
Swiss-port # Q9GZZ6 Human Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-10 |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | CHRNA10 |
| Gene Full Name | cholinergic receptor, nicotinic, alpha 10 (neuronal) |
| Function | Ionotropic receptor with a probable role in the modulation of auditory stimuli. Agonist binding may induce an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane. The channel is permeable to a range of divalent cations including calcium, the influx of which may activate a potassium current which hyperpolarizes the cell membrane. In the ear, this may lead to a reduction in basilar membrane motion, altering the activity of auditory nerve fibers and reducing the range of dynamic hearing. This may protect against acoustic trauma. [UniProt] |
| Cellular Localization | Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 50 kDa |
Images (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In