ARG56375
anti-CKAP4 antibody
anti-CKAP4 antibody for ICC/IF,Western blot and Human,Mouse,Rat
Overview
| Product Description | Rabbit Polyclonal antibody recognizes CKAP4 |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu, Ms, Rat |
| Tested Application | ICC/IF, WB |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Target Name | CKAP4 |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of Human CKAP4 |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | ERGIC-63; p63; CLIMP-63; Climp-63; 63-kDa cytoskeleton-linking membrane protein; Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. | ||||||
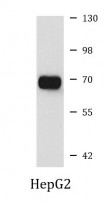
| Positive Control | HepG2 |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Affinity purification with immunogen. |
| Buffer | PBS (pH 7.3), 0.02% Sodium azide and 50% Glycerol. |
| Preservative | 0.02% sodium azide |
| Stabilizer | 50% Glycerol |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | CKAP4 |
| Gene Full Name | cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 |
| Function | High-affinity epithelial cell surface receptor for APF. Mediates the anchoring of the endoplasmic reticulum to microtubules. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 66 kDa |
| PTM | Reversibly palmitoylated. Palmitoylation at Cys-100 by DHHC2 is required for its trafficking from the ER to the plasma membrane and for its perinuclear localization. Increased phosphorylation during mitosis prevents binding to microtubules. |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In