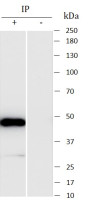
ARG44709
anti-MVK antibody
anti-MVK antibody for Immunoprecipitation,Western blot and Human
Overview
| Product Description | Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes MVK. |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Tested Application | IP, WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2b |
| Target Name | MVK |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | Mevalonate kinase; EC 2.7.1.36; POROK3; MK; MVLK; LRBP |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Protein A purification |
| Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or below. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | MVK |
| Gene Full Name | mevalonate kinase |
| Background | This gene encodes the peroxisomal enzyme mevalonate kinase. Mevalonate is a key intermediate, and mevalonate kinase a key early enzyme, in isoprenoid and sterol synthesis. Mevalonate kinase deficiency caused by mutation of this gene results in mevalonic aciduria, a disease characterized psychomotor retardation, failure to thrive, hepatosplenomegaly, anemia and recurrent febrile crises. Defects in this gene also cause hyperimmunoglobulinaemia D and periodic fever syndrome, a disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of fever associated with lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, gastrointestinal dismay and skin rash. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2014] |
| Function | May be a regulatory site in cholesterol biosynthetic pathway. [UniProt] |
| Cellular Localization | Cytoplasm. Peroxisome. [UniProt] |
| PTM | N-glycosylation enhances cell surface expression and lengthens receptor half-life by preventing degradation in the ER. |
Images (2) Click the Picture to Zoom In