ARG23665
anti-DLL1 antibody [HMD1-5] (PE)
anti-DLL1 antibody [HMD1-5] (PE) for Flow cytometry and Mouse,Rat
Overview
| Product Description | PE-conjugated Hamster Monoclonal antibody [HMD1-5] recognizes DLL1. This product specifically recognizes Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1), one of the five major ligands of the Notch signaling pathway, which is activated through the binding of specific ligands to the Notch receptors Notch 1-4.The Notch signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved pathway in multi-cellular organisms, which is vital for cell-cell communication, important during fundamental developmental and physiological processes, including regulation of cell fate decisions during neuronal, cardiac and endocrine development, stem cell hematopoiesis, thymic T-cell development, and both tumor progression and suppression. Ligation of Notch receptors by their specific ligands, Jagged1 (CD339), Jagged2, Delta-like protein 1 (DLL1), DLL3 and DLL4, on physically adjacent signal receiving cells, induces proteolysis of the receptors by ADAM-family metalloproteases and the gamma-secretase complex, within the transmembrane domain, releasing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) to translocate to the nucleus. Subsequent signal transduction then occurs through either the CSL-NICD-Mastermind complex cascade (canonical pathway), or NF-kappaB-NICD and CSL-NICD-Deltex complex signaling cascades (non-canonical pathway). The canonical pathway inhibits the differentiation of stem cells or progenitor cells, whilst the non-canonical pathway promotes differentiation. DLL1 is widely expressed, and acts as a mediator of cell fate decisions during hematopoiesis, and may play a role in cell-to-cell communication in mammalian embryos. DLL1 plays an important role in B and T cell differentiation, in embryonic somite formation and patterning, and associates with the scaffolding protein MAGI1 at adherens junctions on neuronal processes. Signaling through DLL1 and Notch 2 has been implicated in the development of marginal zone B cells (MZB). Hamster anti Mouse Delta-Like Protein 1 antibody, clone HMD1-5 blocks binding of Notch2 to Dll1 (Moriyama et al. 2008) |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Ms, Rat |
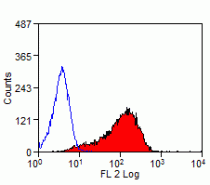
| Tested Application | FACS |
| Host | Hamster |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | HMD1-5 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Target Name | DLL1 |
| Antigen Species | Mouse |
| Immunogen | DLL1-expressing CHO cells. |
| Conjugation | PE |
| Alternate Names | DELTA1; H-Delta-1; Drosophila Delta homolog 1; Delta-like protein 1; DL1; Delta1; Delta |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | FACS: Use 10 µl of the suggested working dilution to label 10^6 cells in 100 µl. * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Purification with Protein G. |
| Buffer | PBS, 0.09% Sodium azide, 1% BSA and 5% Sucrose. |
| Preservative | 0.09% Sodium azide |
| Stabilizer | 1% BSA and 5% Sucrose |
| Storage Instruction | Aliquot and store in the dark at 2-8°C. Keep protected from prolonged exposure to light. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | DLL1 |
| Gene Full Name | delta-like 1 (Drosophila) |
| Background | DLL1 is a human homolog of the Notch Delta ligand and is a member of the delta/serrate/jagged family. It plays a role in mediating cell fate decisions during hematopoiesis. It may play a role in cell-to-cell communication. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Function | Acts as a ligand for Notch receptors. Blocks the differentiation of progenitor cells into the B-cell lineage while promoting the emergence of a population of cells with the characteristics of a T-cell/NK-cell precursor. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 78 kDa |
| PTM | Ubiquitinated by MIB (MIB1 or MIB2), leading to its endocytosis and subsequent degradation (By similarity). Ubiquitinated; promotes recycling back to the plasma membrane and confers a strong affinity for NOTCH1. Multi-ubiquitination of LYS-613 by MIB1 promotes both cis and trans-interaction with NOTCH1, as well as activation of Notch signaling. Ubiquitinated by NEURL1B (By similarity). Phosphorylated in a membrane association-dependent manner. Phosphorylation at Ser-697 requires the presence of Ser-694, whereas phosphorylation at Ser-694 occurs independently of the other site. Phosphorylation is required for full ligand activity in vitro and affects surface presentation, ectodomain shedding, and endocytosis. O-fucosylated. Can be elongated to a disaccharide by MFNG. [UniProt] |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In