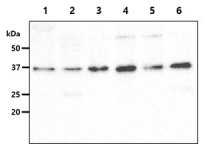
ARG57064
anti-GALE antibody [6G10]
anti-GALE antibody [6G10] for Western blot and Human
Overview
| Product Description | Mouse Monoclonal antibody [6G10] recognizes GALE |
|---|---|
| Tested Reactivity | Hu |
| Tested Application | WB |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone | 6G10 |
| Isotype | IgG1, kappa |
| Target Name | GALE |
| Antigen Species | Human |
| Immunogen | Recombinant fragment around aa. 1-348 of Human GALE. |
| Conjugation | Un-conjugated |
| Alternate Names | UDP-GlcNAc 4-epimerase; SDR1E1; UDP-galactose 4-epimerase; Galactowaldenase; EC 5.1.3.2; EC 5.1.3.7; UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-GalNAc 4-epimerase; UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-epimerase; UDP-glucose 4-epimerase |
Application Instructions
| Application Suggestion |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Note | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
Properties
| Form | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Purification | Purification with Protein A. |
| Buffer | PBS (pH 7.4), 0.02% Sodium azide and 10% Glycerol. |
| Preservative | 0.02% Sodium azide |
| Stabilizer | 10% Glycerol |
| Concentration | 1 mg/ml |
| Storage Instruction | For continuous use, store undiluted antibody at 2-8°C for up to a week. For long-term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C. Storage in frost free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Note | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
Bioinformation
| Database Links | |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | GALE |
| Gene Full Name | UDP-galactose-4-epimerase |
| Background | This gene encodes UDP-galactose-4-epimerase which catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose, and the epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. The bifunctional nature of the enzyme has the important metabolic consequence that mutant cells (or individuals) are dependent not only on exogenous galactose, but also on exogenous N-acetylgalactosamine as a necessary precursor for the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Mutations in this gene result in epimerase-deficiency galactosemia, also referred to as galactosemia type 3, a disease characterized by liver damage, early-onset cataracts, deafness and mental retardation, with symptoms ranging from mild ('peripheral' form) to severe ('generalized' form). Multiple alternatively spliced transcripts encoding the same protein have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| Function | Catalyzes two distinct but analogous reactions: the reversible epimerization of UDP-glucose to UDP-galactose and the reversible epimerization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine. The reaction with UDP-Gal plays a critical role in the Leloir pathway of galactose catabolism in which galactose is converted to the glycolytic intermediate glucose 6-phosphate. It contributes to the catabolism of dietary galactose and enables the endogenous biosynthesis of both UDP-Gal and UDP-GalNAc when exogenous sources are limited. Both UDP-sugar interconversions are important in the synthesis of glycoproteins and glycolipids. [UniProt] |
| Calculated MW | 38 kDa |
Images (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In